As part of my commitment to providing you with the knowledge and resources to navigate the complex world of finance with ease, I am pleased that you can now download four indispensable guides that cover a range of important financial topics.
Unlock Your Financial Success with Our Exclusive Guides!
By Peter Brooke
This article is published on: 3rd July 2023

- Understanding Investment Risk
- French Tax Changes and Planning Opportunities for 2023
- Responsible Investing and ESG Funds – The Spectrum Approach
- Unveiling the Benefits of Assurance Vie – Tax Efficient Saving and Investments in France
To access these resources, simply click on each of the links.
I am a firm believer that knowledge is the key to financial success, and these guides are designed to empower you on your financial journey. Whether you’re an experienced investor or just starting out, these guides offer valuable insights to help you make well-informed decisions.
Understanding Investment Risk
Investing can be both rewarding and challenging – in this guide, we try to demystify investment risk. I believe risk can be thought of like energy: it is neither created nor destroyed, it simply changes from one category to another.
↵Click the image to find out more.
French Tax Changes and Planning Opportunities for 2023
Taxation is a crucial aspect of financial planning, particularly if you reside in France or have financial ties to the country. Our guide summarises the current French tax landscape for 2023 – providing you with an overview of tax changes and planning opportunities.
↵Click the image to find out more.
Responsible Investing and ESG Funds – The Spectrum Approach
Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) investing has gained significant momentum, allowing investors to align their portfolios with their values. This guide delves into the world of sustainable investing, providing insights into ESG principles, investment strategies, and the potential impact of ESG factors on financial performance.
↵Click the image to find out more.
Tax Efficient Savings & Investments in France 2023
Unveiling the Benefits of Assurance Vie
Assurance Vie is a popular long-term savings and investment product in France. Discover the advantages, tax benefits, and investment options associated with Assurance Vie in our comprehensive guide. Learn how to leverage this powerful tool to secure your financial future.
↵Click the image to find out more.
Remember, I am here to support you. If you have any questions or need further assistance, please feel free to reach out via the below contact form, or the booking system below.
Reducing Spanish tax
By John Hayward
This article is published on: 27th June 2023

Use a beneficial savings structure
Investing money is often seen as a risky thing to do even though it is generally understood to be necessary. For example, those receiving pension income would not be in the same position if the companies paying the income had left all of the pension contributions in a current account or in a box under the bed.
Financial markets can be volatile (always, I hear you shout). We fully appreciate this. We also acknowledge that inflation has created higher interest rates. Better news if you are a saver but not so pleasant for mortgage payers, or parents having to help their children pay off increased debt.
Let us imagine that, for the foreseeable future, we have high inflation accompanied by higher interest rates. Using an amount of £500,000, I have compared depositing in a savings account with investing in a Spanish compliant investment bond and I have used an interest/growth rate of 4%. I have based my comparison on the bond paying growth to the bondholder’s bank account and using GBP as I cannot see any Euro accounts paying 4%.
– £500,000 at 4% = £20,000
– Using an exchange rate of 1.16 £/€,
– £20,000 = €23,200
The deposit account interest is taxed in full and, at current 2023 rates, is €4,752 each year. This has to be declared in the annual tax return.
The Spanish compliant bond attracts tax on the gain within the withdrawal. I have based the calculation on the same amount being withdrawn i.e., €23,200. In the first year, the taxable gain within this is only €892 and the corresponding tax is €170. The taxable amount within the bond income increases over time but, over 10 years, the tax is:
– €47,520* on the deposit account interest
– €8,381* on the bond income
This gives a tax saving of over €39,000 over 10 years by using the Spanish compliant bond.

If no money is withdrawn from the bond, no tax is payable whereas the interest on the deposit account will continue to be taxed.
If the bondholder moved back to the UK, and nothing had been withdrawn whilst living in Spain, any growth on the bond whilst resident in Spain would be ignored by the UK tax office.
As an added benefit of reducing taxable income, wealth tax can be reduced. See this Wealth Tax in Spain article.
There can also be inheritance tax benefits with the bond when compared to the deposit account.
Well managed portfolios have consistently outstripped inflation. Conversely, deposit interest rates offered to savers have consistently under-performed inflation over the years.
To find out how we can help you with your existing investments and tax planning, and provide you with ideas for the future, contact me today at john.hayward@spectrum-ifa.com or on +34 618 204 731 (WhatsApp)
* E&OE. The above is a simplified example for illustrative purposes and general guidance only.
How to reduce Wealth Tax in Spain
By John Hayward
This article is published on: 21st June 2023

Earlier this year, I wrote an article about the introduction of solidarity tax in Spain. This is a “temporary” (we shall see) tax on wealth for those with more than €3,000,000 in assets. This is in addition to wealth tax although any wealth tax due can be deducted from the solidarity tax bill. (This is not the case for residents of the Madrid or Andalusia regions as there is no Wealth Tax currently).
I have been working with clients who are affected by these taxes, trying to find ways of reducing the tax liability. Reducing wealth by gifting to, say, children is an option but that can create additional immediate tax problems. Also, for a number of different reasons, some clients are not willing to gift anything in their lifetime.
The amount of wealth Tax that has to be paid can be governed by income. Your income tax and wealth tax cannot exceed 60% of your total taxable income.
Example:
– Total taxable income is €40,000
– Tax payable €8,000
– Assets subject to wealth tax €3,000,000
– Wealth tax due €39,000
– The maximum that can be paid when adding income tax and wealth tax together is 60% of the total taxable income (€40,000).
– €40,000 x 60% = €24,000
Therefore, the maximum wealth tax that can be paid is €16,000 (€24,000 less €8,000 income tax).

However, having to pay €16,000 a year in wealth tax is still not particularly nice. What we can do is look at the income in order to see if this can be restructured. Notable targets for this type of planning are savings interest (more relevant at the moment) and income/dividends from shares and investment funds. By careful planning, we can provide the same level of income yet reduce the tax. Please visit this Tax Benefits of a Bond page which illustrates one of the major benefits of a correctly structured investment bond which not only reduces income tax but also helps to reduce wealth tax.
To find out how we can help you with your existing investments, pensions, and tax planning, and provide you with ideas for the future, contact me today at john.hayward@spectrum-ifa.com or on +34 618 204 731 (WhatsApp)
Financial update June 2023
By Katriona Murray-Platon
This article is published on: 19th June 2023

Tax season is drawing to a close. However this year there is still something you need to make sure you have done before you can get out there and enjoy the summer weather.
You may still need to do the property declaration that I mentioned in my February edition. The declaration service has been available for several months now and so enough time has passed to be able to address some of the issues that have arisen.
Just as a reminder, if you own a property, and therefore pay taxe foncière, you have to declare the buildings on the land you own if they existed on 1st January. Because the Taxe d’habitation has been scrapped for main residences the French authorities want to find out which buildings are occupied and rented (even if just for holidays) which will allow them to more accurately establish the taxe d’habitation on second homes this autumn.
You must declare anyone who is occupying a property which belongs to you, even if it is a family member living there for free. However if you are only renting a room in your house, you do not need to declare this separately.

If the ownership of the property is divided between the bare owners (nu proprietaries) and the beneficiaries (usufruitiers) it is the latter who should declare the property on their online tax account.
You may have noticed that any outhouses, sheds and garages also appear on the declaration. If these have been converted to be rented or are simply let as parking spaces, they still need to be declared. A garage that is less than 1km from the main house is considered as adjacent to the property and therefore may be included in the surface area calculation for the taxe d’habitation.
The declaration can only be done online. If you do not have access to the internet (or know someone who doesn’t) or if you or they are really having problems completing this form online, you can call the tax office on the number below or make an appointment with your local tax office and they can assist you. Some post offices also have someone there who can help you with administrative matters.
If you have any problems with the declaration you can call the tax office on 0809 401401 or use the messenger service and the drop down menu to select the problem.
If you have an elderly resident who has gone into a home but has kept their former home and it is rented, they still need to declare it. There is an exemption from taxe d’habitation for residents of retirement homes (Ehpads).
If you rent a property you have to declare what kind of rental it is (long term or holiday let) and the identity of your tenants but you don’t need to declare the actual rent received just yet, this will only become mandatory in 2025.
You have until the end of June to complete this declaration so do take your time to make sure that the information is correct.
As always if you have any questions on this or any other matters please do get in touch!
Taxes and property in Portugal
By Mark Quinn
This article is published on: 15th June 2023

Many expats will be surprised to discover that even when selling their main home in Portugal, Capital Gains Tax (CGT) applies.
They may also not realise that when selling secondary or rental properties, tax is likely to be due in both Portugal and the country where the property is located. So, what do you need to know?
CGT
Portuguese residents are subject to CGT on their worldwide property gains. On the sale of Portuguese property, the tax treatment is the same for Non-Habitual Residents (NHR) and non- NHRs; 50% of the gain is added to your other income in
that tax year and taxed at scale rates.
For overseas property, there is no tax due in Portugal for NHRs but there is tax due (in the same manner as above) for non-NHRs. CGT is also likely due in the country where the property is located.
Can you mitigate any tax?
Despite the potential for eye-watering tax levels, some reliefs are available if the property you are selling is your home. The two mentioned reliefs can be used in isolation or conjunction.
- Main residence relief: You can mitigate all (or a portion of) the CGT by reinvesting the sale proceeds (not just the gain) into another property in the EU or EEA. Any amount not reinvested is taxed
- Reinvestment into a qualifying savings structure: This is a relatively recent relief and is particularly advantageous for those wishing to downsize (and therefore will not fully reinvest the sale proceeds), or for those moving back to the UK or elsewhere outside of the EU/EEA. There are strict criteria for qualification and we can advise on this area
NHR tax opportunity
For those with overseas property portfolios, selling these during the 10-year NHR period is much more tax efficient as the gain is exempt from CGT in Portugal. But hat about the tax due in the country the property is located? Let’s look at UK property as an example.
The UK only applies CGT to gains accumulated since 6th April 2015 and you will also have your annual UK CGT allowance to deduct (additional reliefs may also apply depending on your situation). If you bought an investment property in joint names in 1992 for £100,000 and it was sold today at £1m, ordinarily tax would be due on the £900k gain. But selling this as a non-UK resident, and assuming linear growth, you only pay tax on the gain since April 2015 i.e. £210,000.
You can effectively ‘wash out’ a large part of the gain simply by selling as a Portuguese tax resident and generating cash to fund your lifestyle.
Portugeuse residency and taxes
By Mark Quinn
This article is published on: 12th June 2023

Residency, domicile, visas and non-habitual residency… it can be confusing. Mark Quinn and Debrah Broadfield of the spectrum IFA group explain NHRs generous tax breaks, tax planning opportunities, and how to reduce or even eliminate income and gains tax on savings and investments.
Legal residence
Legal residence relates to the right to reside in a particular country. If you are an EU citizen, you have the automatic right to reside in any other EU country without the necessity for a visa. If you are coming from outside the EU, you must apply for a visa to establish your residency rights – a common visa route is the D7 or ‘passive income visa’.
Legal residence is important as it determines how long you are allowed to spend in a country and your right to benefits such as healthcare and social security. Legal residence however does not impact or determine your tax status.
Tax residency
Generally, tax residency is determined by your physical presence in a country and Portugal, along with many other countries, uses the 183-day rule for determining tax residency.
Understanding your tax residency is important because it determines which country has taxing rights over you and can avoid double-taxation issues when you have links to more than one jurisdiction.
It is possible to have legal residence in Portugal, but not actually be Portuguese tax resident e.g. if you have the right to stay in Portugal but you do not spend enough time in Portugal in a given year to be considered tax resident.
Non-Habitual Residence (NHR)
NHR gives successful applicants a special tax status in Portugal for 10 years, but its name is somewhat misleading. ‘Non-habitual’ actually refers to the requirement that you must not have been resident in Portugal in the five years prior to application.
You must apply for residency before you can apply for NHR. On obtaining residency, you have until the following 31st March to apply for NHR. If you miss this deadline there is no second chance to apply.

Domicile
Domicile is something that is often confused with residency. Your domicile does not affect your income tax position, but it does affect your liability to UK Inheritance Tax. It is most likely to be a consideration for British nationals, individuals married to British nationals, or those who are not British but spend a considerable amount of time in the UK.
UK domicile is very adhesive and is difficult to shed; moving to Portugal does not automatically remove your liability to UK inheritance tax, no matter how long you have been out of the UK. Likewise, simply sheltering the bulk of your assets in a trust or QNUPS is unlikely to protect assets from UK IHT.
Tax liabilities in Portugal
Tax residents of Portugal must declare their worldwide income and gains in Portugal. For those with assets in several countries, you might also have tax and reporting obligations in the jurisdictions where you hold the assets e.g. UK rental income is always taxable in the UK but is also reportable and taxable in Portugal. Whether you will pay tax twice depends on the Double Taxation Treaty between the two countries, but there are usually rules in place to avoid this happening.
Potential pitfalls
Many people believe that, as long as they are paying tax somewhere they are meeting their obligations, but this is not correct. It is important that you have a clear understanding of where you are resident to avoid being taxed in more than one jurisdiction or being fined.
Registering yourself in Portugal does not automatically make you a tax resident. It is determined by your physical presence, so it is important to check your tax residency every tax year, as it could change.
Your nationality or citizenship does not change by coming to live in Portugal and becoming resident, although you do have the option of applying for Portuguese citizenship after five years.
Financial Top Tips in Spain
By Chris Burke
This article is published on: 11th June 2023

Thanks to everyone for their positive feedback on these newsletters. They are purely to give us ‘foreigners’ the heads up on financial matters that are at best opaque here in Spain. Before I head off to a chiringuito, as it’s that time of year, this month we shall be concentrating on the following important topics:
- National Insurance deadline to backdate/buy years in the UK – act now!
- What pension are you likely to receive as self-employed/autonomo here in Spain?
- How much money do I need to retire (with example) comfortably?
- Legal aid in Spain for British nationals
UK National Insurance deadline approaching
I meet many people who have contributed into the UK state pension (National Insurance contributions) and then move abroad. They may also pay into other countries´ state pensions, but the BIG potential issue is that no one knows for sure if these will be combined and what income in retirement you will receive. Some people say ‘Well they have to, otherwise it’s not fair and that’s how it works now/used to before Brexit’. I tend to focus on as many certainties as possible and always try to have a ‘more guaranteed’ plan instead of relying on what governments do and don’t do, as that doesn’t fill me with confidence.
I have met many people with 5 years’ state contributions here, 10 there and another 5 somewhere else and they don’t actually end up receiving ANY state pension. This is not the situation I want to end up with and that’s why I recommend to anyone who has existing UK NI contributions to continue to contribute to them, aiming to reach the maximum years needed to receive a full UK state pension. As a non-UK resident, if you are paying taxes in Spain it´s normally £12 a month to contribute to the UK system – for me it’s a no brainer.
With that in mind, normally you can ‘backdate’ or buy past years’ contributions to fill in any gaps you may have. However, from the end of July (next month), you will only be able to backdate 6 years, whereas before this deadline you can buy more. So, if you have significant gaps in your UK NI contributions you only have until next month to ‘fill’ a part of them. You can find out more here: National Insurance Gaps
Self-employed/autonomo state pension amounts
I wanted to clarify something that not many people here realise when they contribute into the social system as self-employed. In the UK you pay your contributions and the number of years you have contributed dictates, more often than not, how much you receive. However, this is not the case in Spain.
Many people are autonomo here and presume the monthly payment they make to the social security, if made over the necessary number of years, (currently 35), will give them the full Spanish state pension – unfortunately that is incorrect. That is because it’s not JUST the number of years you contribute, but also the amount you pay. Not many accountants will confirm that there is a choice on how much you can pay each month towards your social security – a low, medium or high amount. Therefore, most people pay the low amount for many years and only realise the problem when they start looking closer, usually at retirement age. I hope most people are sitting down when I tell you that if you paid the minimum contributions for the full number of qualifying years in Spain, you would receive around €643 a month, (almost half of the UK amount), whilst the maximum is €2,617.
That is why I recommend to almost everyone that they ensure as far as possible that they are fully contributed into the UK system by retirement.
Here are the links to HMRC to read about and organise this, (please don’t get in touch with me for help as it has to be done by yourself):
- Information on paying National Insurance contributions from abroad – gov.uk/national-insurance-if-you-go-abroad
- The Form to complete to pay Class 2 voluntary contributions at £12 a month – gov.uk/government/publications/social-security-abroad-ni38
You can obtain a state pension forecast here in Spain if you have a digital certificate here
As a local accountant recently told me, and I quote, “My personal opinion is that it is better that you make your own pension, saving the money and investing it directly, and more because each time the pensions are reduced year by year and it is quite sure that in the future they will be reduced most, but this is only my opinion…… This is what I decided to do a long time ago.”
So, my advice? Pay the minimum here, pay your NI in the UK and reach the maximum alongside making your own provision along the way.

How much money do you need for a comfortable retirement?
Now, this is a very difficult forecast to make given everyone’s very different lifestyles, so I must use a few assumptions based on the following:
- Average annual salary – €3,000 per month after tax
- Medium lifestyle choice in retirement
Therefore, one could surmise an income needed in retirement of €4,000 per month before tax could be the average amount required. If we say you receive the full state pension of around €1,000 per month, you need to supplement €3,000 per month.
If you had €300,000 and it gave you 5% return each year this would give you €1,250 per month – so we still need another €1,750 per month. Of course, this means that as you are taking the full interest earned from your money pot it is not keeping up with inflation. Therefore, taking 4% at most is more applicable which gives you €1,000 per month income. However, if this income falls under income tax (such as property income), then from earnings upwards of the current allowance of €6,700 each year at age 65 in Spain you will be taxed. Adding that to the state pension, (which is declarable for income tax in Spain), we probably need to say it’s more likely €800 a month net from this monetary income.
So, we see the problem, what do we need to do? In essence, make your savings/monies and assets work for you over the years with professional management, taking into account tax mitigation. The more money you invest and the longer the time, the more comfortable or higher probability you will achieve your goals.
By the way, the answer to the above question also depends on how you are receiving the income. Tax efficient savings will greatly reduce you tax liability away from income tax to the lower, (and with possible offsetting capability) of capital gains tax. In monetary terms, to be safe I would suggest €800,000 plus a property rented out in retirement, in today’s money, as an income will safely achieve this. Is that the average persons situation?
Legal aid in Spain for British nationals
The UK has just released the following information on legal aid available for those residing in Spain which is perhaps ‘better’ than I would have expected and well worth knowing: Legal Aid Spain
Click here to read independent reviews on Chris and his advice.
If you would like any more information regarding any of the above, or to talk through your situation initially and receive expert, factual based advice, don’t hesitate to get in touch with Chris.
Inheritance tax liabilities in Portugal
By Mark Quinn
This article is published on: 7th June 2023

Our team of advisers in Portugal talk about the inheritance tax (IHT) implications of leaving the UK and point out that British nationals are likely to remain liable to UK IHT even many years after departure.
To understand why UK nationals have a liability to IHT we must understand the concept of domicile.
There are actually four types of domicile, but relevant to most readers will be ‘domicile of origin’. Generally, you acquire your domicile of origin from your father – if he is British, you have a UK domicile and it is this that gives you your liability to IHT.
It is important to understand that domicile is different from tax residency; residency is based on your physical location – you can be a Portuguese tax resident and live in Portugal, never return to the UK but still have a UK domicile by virtue of your origin. The main impact of domicile is that it determines your liability to UK IHT. Simply, if you are UK domiciled, then you are liable to UK IHT. Moreover, IHT is based on your worldwide assets so, whether it be an Australian property or a bank account in the Cayman Islands,
It is all caught within the UK IHT tax ‘net’.
If you are UK domiciled and your worldwide estate is subject to IHT on death, and you are resident in Portugal, you could also have a Portuguese tax liability. Portugal, however, only taxes assets that are located in Portugal, eg property, and that pass to non-direct line ascendants or descendants. The UK/Portugal double tax treaty does not cover IHT and there is no automatic relief applied, so it is worth noting that there is a risk that double taxation might apply.

Can you avoid UK IHT?
Most people find IHT the most distasteful tax of all because, after working hard and having paid income tax, capital gains tax, stamp duty, VAT, etc, throughout their lives, the final ‘nail in the coffin’ is that the UK exchequer will take 40% of your estate on death.
- The simplest way to mitigate UK IHT is to gift assets during your lifetime. You can gift an unlimited amount to beneficiaries and pay no tax if you survive seven years from the date of the gift – this is known as a ‘potentially exempt transfer’. Be careful, however, that you fully surrender the rights and enjoyment of the asset because if not, it will remain in your estate for UK IHT purposes eg gifting property to your children but still living in it for free or at a reduced market rent.
- You can also take advantage of other gifting exemptions, such as your annual allowance of £3,000 or ‘gifting out of normal expenditure’ – if you can demonstrate you have surplus income to your needs, you can regularly gift the excess each year and this will fall immediately outside of your estate.
Whilst gifting is simple, some may not be comfortable relinquishing control just yet, so you could consider investment options such as a Qualifying Non-UK Pension Scheme (QNUPS). However, be careful, as if HMRC believe this is done for tax avoidance purposes, or it cannot be proved that it wasn’t, they can still tax this, so it must be managed carefully’.
You can ‘shed’ your UK domicile of origin by acquiring a new ‘domicile of choice’. You do this by moving to a new country and demonstrating your intention to remain there permanently. However, whilst it is easy to move country and change your tax residency, proving your intention is more challenging. HMRC does not have a prescribed list of ‘dos and don’ts’ but everything you do, say and leave behind can be used as evidence of your intention. Consider the case of Richard Burton, who after decades of living in Switzerland was deemed to have not shed his UK domicile because he had the Welsh flag draped over his coffin and was buried with a book of Dylan Thomas’s poems. HMRC successfully argued that he never truly severed ties with his ‘homeland’, Wales.
HMRC will not provide a certificate or determination of domicile during your lifetime, therefore meticulous recordkeeping is essential. It is the executors of your estate who will be presenting your non-domicile case after your death, as this is when a challenge might arise.
History: How it can save you money
By John Hayward
This article is published on: 31st May 2023

“If you think you have it tough, read history books.” Bill Maher
I was not particularly interested in history at school, mainly because the history masters (I went to a grammar school where we were taught by masters in moth-eaten gowns and who wore their ties outside their jumpers) would want to teach us about aspects that I had absolutely no interest in.
The Dark Ages, for example. They are called dark ages for a reason. These days I will happily surf the web (can we still say that?) going off-piste (no holding me now) and finding out brilliant historical facts that I am interested in and not what I am told to be interested in. Or maybe I am being told, in this Artificial Intelligence world that we now live in. Having said that, I have not felt any pressure to learn any more about the dark ages.
What is my point here? History is important because it can help us to make decisions. The problem is that, although we have plenty of information to refer to, and perhaps have taken on board, we all too often forget, or even choose to ignore, the “lesson”. In the investment world, it appears that everything that is happening now never occurred before. Or maybe it did but in a dark age when nobody was literate enough to write down what was going on.
Sell low, buy high. Isn’t that a ridiculous investment strategy? It seems not, to some. I have been in the company of many people over the years who believe that they know when to sell and when to buy back in when “things are better/markets have settled/it is less rainy/the dog has been to the vet”. This strategy has consistently proven itself to be flawed. Although past performance is no guarantee of future performance, history can give us an idea of what could happen in the investment world after different global events. In more recent years, the financial crisis of 2008 and Covid-19 in 2020 have been big tests. After both “incidents”, those who stuck with it have been better off.
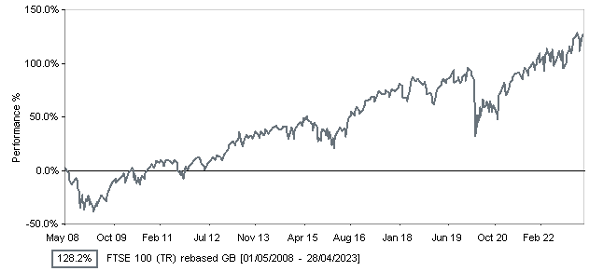
Source: Financial Express
Focusing on a stock market index that many British people are familiar with, the FTSE100, in the last 15 years to 1st May 2023, there have been 4 years that have been negative. I apologise for spelling this out but that means 11 years have been positive. 11-4. I like that score. The average annual gain of the index over that period has been almost 13%. Even more interesting is the tendency that a bad year is followed by an outstanding one. This is why, when people sell, they crystallise a loss and then possibly miss the best part of any recovery.
I understand that not everybody is comfortable with sitting out large falls (2008 and 2020). To cater for this, we have solutions within our armoury which limit the downside whilst still providing long-term growth.
To find out how we can help you with your existing investments, and/or provide you with ideas for the future, contact me today at john.hayward@spectrum-ifa.com or on +34 618 204 731 (WhatsApp)
If you are feeling down, pick up a history book. It is certain to take your mind off your woes.
How is France doing?
By Richard McCreery
This article is published on: 17th May 2023

If you live in France, the general impression you might have is of a country that is dragged down by strikes and protests, that the cost of living is soaring and the dream of retiring whilst still young is under threat. But it is not all bad news. If you have investments in France, or are planning to retire here, there are several reasons to be cheerful about the state of the country.
Despite fears of a possible recession, France’s GDP grew 0.2% in the latest quarter and was 0.8% higher than a year earlier – not exactly blowing the lights out but coping reasonably well with Eurozone interest rates that have risen to 3.75%. In fact, you can still get a 20-year mortgage in France and pay less than 3%, so the housing market is not coming under the same pressure as it is in some countries like the US, where a typical mortgage now costs 6.5%, or Sweden, where house prices have fallen sharply.
At 7.2%, France’s unemployment rate is around the lowest level it has been for several decades. The more people in work, the better. Inflation may be historically high at 5.9% but this is lower than the Eurozone average of 7% and considerably less painful than the UK’s 10.1% rate. We were very lucky that the government capped energy price rises at 4% last year and 15% this year.
Where France has more of a problem is its debt levels, partly because of that low retirement age but also because of the government’s generosity during the pandemic, although France is hardly alone in this. France’s government debt-to-GDP ratio has swelled from 97% in 2019 to 111% today. It is because France’s national debt has grown to almost 3 trillion Euros, and because it is so hard for the government to do anything about it without triggering widespread rioting, that the rating agency Fitch recently downgraded the country’s credit rating to AA- (outlook: Stable). This still leaves it slightly better off than the UK, whose outlook is Negative.
But President Macron is making efforts to build on France’s substantial industrial base, asking Elon Musk and other business leaders to invest in the country. In fact, according to accounting firm EY, France is the most attractive country in Europe for foreign investment and has been for four years in a row. It is also the home of LVMH, which recently became the 7th largest company in the world, worth more than half a trillion Dollars, as well as Kering (the owner of Gucci) and Hermès. French luxury goods companies are the European stock market equivalent of Big Tech stocks in the US, they seem to go from strength-to-strength and have powered the CAC 40 to a record high this year. French banks also seem to have come through the recent turmoil in the sector relatively unscathed.
France has a great standard of living, it is the world’s number one tourist destination and the economy is on a fairly sound footing. Taxes are high, but residents also have access to very tax efficient investment vehicles that can reduce exposure to income tax and inheritance tax, with the right planning and advice. There is a lot to be said for investing in the EU’s second largest economy. Despite the burning barricades on the nightly news, France is doing fine right now.






