The corrosive effect of inflation and fees
Here we look at two key hurdles to investment performance, and ultimately your lifestyle, and some ways to tackle these issues.
Inflation
This is a topical issue as we all experience the pinch of rising energy, food, and other prices, with inflation in the UK and US recently hitting 7% and 8% respectively.
It is important to monitor and understand as it tells you how much return you need to maintain your current standard of living. So, what can you do to try and beat inflation?
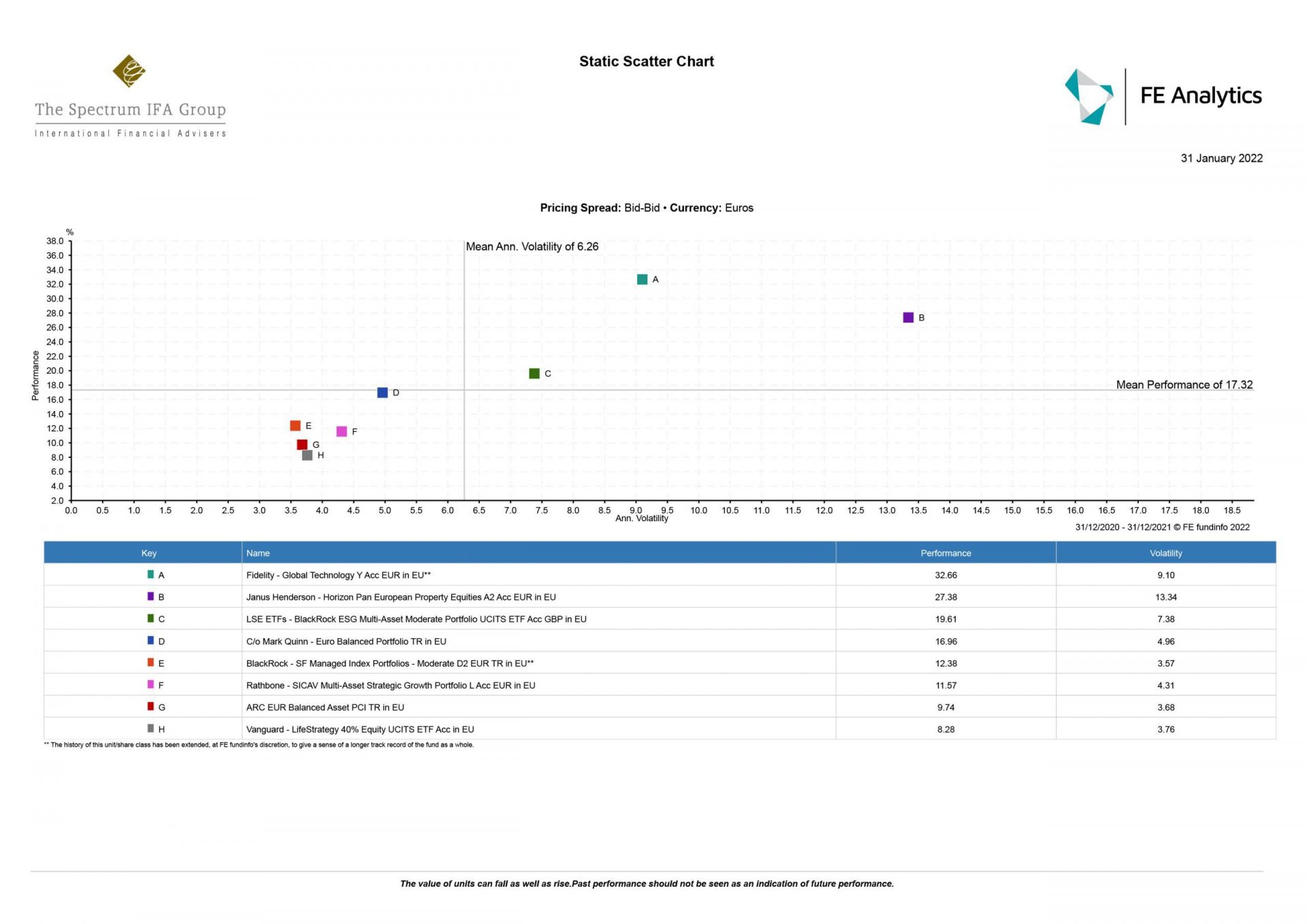
Moving out of cash is critical as you are losing money in real terms. There is no one solution but building a diversified risk-rated portfolio gives you a greater chance of growing your money in excess of inflation over the medium to longer term.
- Shares/equities – as companies and earnings can adjust upwards, shares tend to keep up with inflation better over time than other investments. However, careful selection here is important as you want to select companies that are able to pass on cost increases to consumers
- Index-linked bonds – these are fixed-income investments and their return is linked to inflation rates
- Commodities – you can benefit from the causes of price increases by investing in companies that are involved in the production of raw materials, such as oil and metals
- Gold – can act as a hedge against inflation and also tends to act differently to the above investment types which means it provides diversification, particularly when geopolitical risks come to the fore
These investments do come with different types of risk so you should seek advice on how to minimise and balance these types of risks. It is also important to monitor and measure risks in relation to the returns you achieve.
Fees and expenses
Another factor often overlooked is fees. These may seem small but over time they can have profound long-term effects. You do not just lose the amount of the fees you pay, but you also lose all the growth that you might have received, compounded over years.
For example, assume you have a €1m portfolio paying 6% p.a. If you had no fees to pay, after 25 years, you would have. €4.3m. If you paid 2% p.a. in costs, you would have €2.6m.
Now going further, if you could reduce your overall charge from 2% to 1% p.a., you would have approx. €3.5m. This seemingly small 1% saving is really €793,215 in real terms over 25 years! And this is being paid to someone else, not you.